When abandoning inefficient centralized heating in favor of an individual system, it can be difficult for the landlord to decide which is better: a single-pipe or two-pipe heating system. Let's find out which type of system is better to choose for installation, what is the difference between these connection schemes and how significant it is.
Advantages and disadvantages of one-pipe and two-pipe heating systems
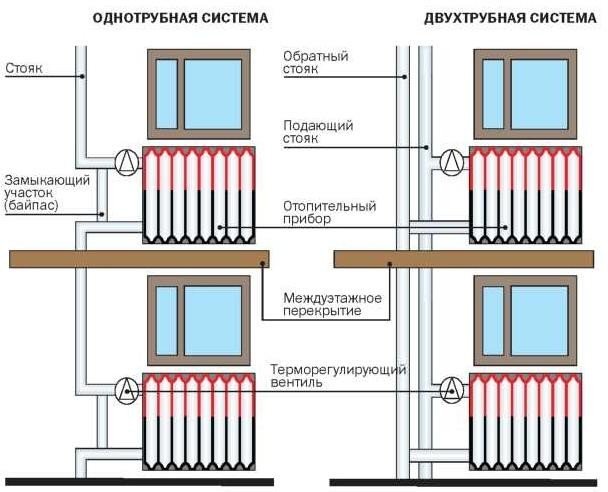
The main difference between the two heating schemes is that the two-pipe connection system is more efficient in operation due to the parallel arrangement of two pipes, one of which supplies the heated coolant to the radiator, and the other drains the cooled liquid.
The scheme of a single-pipe system is a series-type wiring, in connection with which the first connected radiator receives the maximum amount of thermal energy, and each subsequent one heats up less and less.
However, efficiency is an important, but not the only criterion that you need to rely on when deciding to choose one or another scheme. Consider all the pros and cons of both options.
Single pipe heating system
Advantages:
- ease of design and installation;
- savings in materials due to the installation of only one line;
- natural circulation of the coolant, possible due to high pressure.
Flaws:
- complex calculation of thermal and hydraulic parameters of the network;
- the difficulty of eliminating errors made in the design;
- all elements of the network are interdependent; if one section of the network fails, the entire circuit stops working;
- the number of radiators on one riser is limited;
- adjustment of the flow of coolant into a separate battery is impossible;
- high coefficient of heat loss.
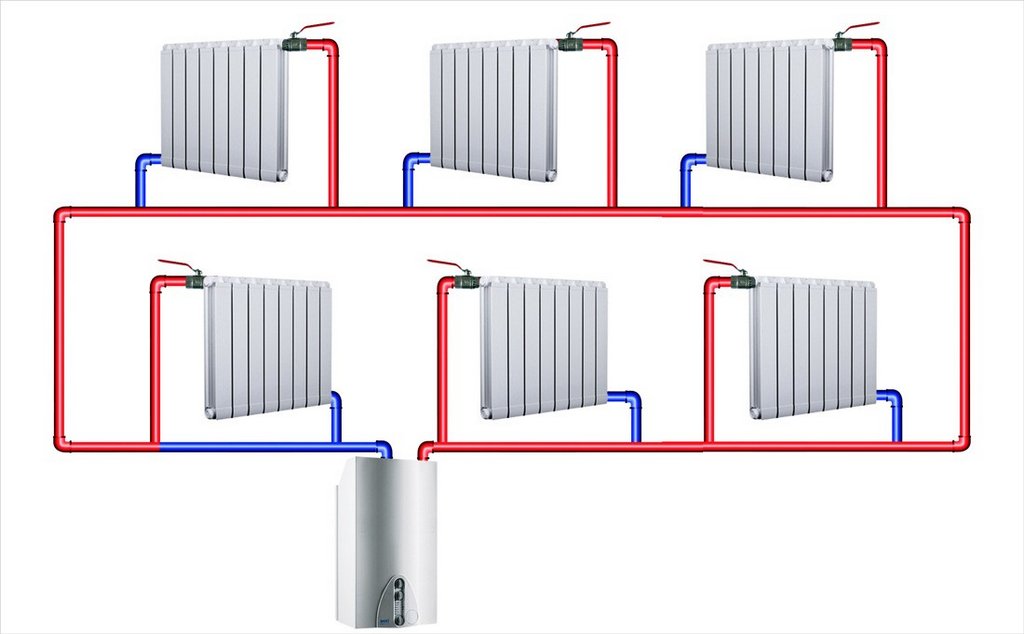
Two-pipe heating system
Advantages:
- the ability to install a thermostat on each radiator;
- independence of the network elements;
- the possibility of inserting additional batteries into an already assembled line;
- ease of elimination of errors made at the design stage;
- to increase the volume of coolant in heating devices, it is not necessary to add additional sections;
- no restrictions on the length of the contour along the length;
- the coolant with the desired temperature is supplied throughout the entire ring of the pipeline, regardless of the heating parameters.
Flaws:
- complex connection scheme compared to single-pipe;
- higher consumption of materials;
- installation requires a lot of time and labor.
Thus, a two-pipe heating system is preferable in all respects. Why do the owners of apartments and houses refuse it in favor of a one-pipe scheme? Most likely, this is due to the high cost of the installation and the high consumption of materials necessary for laying two highways at once. However, one should take into account the fact that a two-pipe system involves the use of pipes of a smaller diameter, which are cheaper, so the total cost of arranging a two-pipe option will not be much more than a single-pipe one.
The owners of apartments in new buildings are lucky: in new houses, in contrast to residential buildings of Soviet development, a more efficient two-pipe heating system is increasingly being used.
Types of two-pipe systems
Two-pipe systems are divided into types depending on:
- type of circuit (open and closed);
- method and direction of water flow (flow and dead ends);
- method of moving the coolant (with natural and forced circulation).
Systems with open and closed circuits
The open-type two-pipe system in city apartments did not take root due to the peculiarity associated with the upper piping, which involves the use of an expansion tank.This device makes it possible to control and replenish the heating system with water, but there is not always a place in the apartment for mounting such a volumetric device.
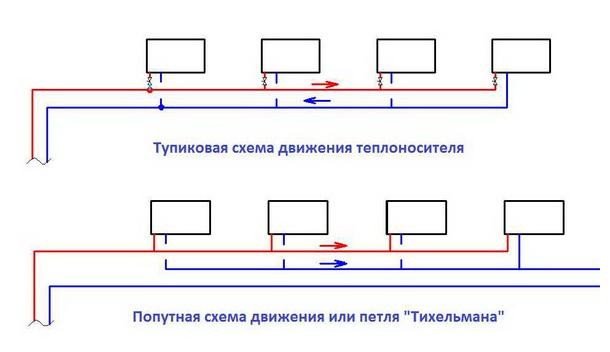
Flow and dead ends
In a flow system, the direction of water flow in the supply and discharge pipes does not change. With a dead-end scheme, the coolant in the supply and return pipes moves in opposite directions. Bypasses are installed in such a network, and radiators are located in closed areas, which makes it possible to turn off any of them without disturbing the heating.
With natural and forced circulation
For natural water circulation, pipes are laid with a mandatory slope; an expansion tank is installed at the top of the system. Forced circulation is carried out by a pump installed in the return pipe. Such a system requires air vent valves or Mayevsky taps.
Components of a two-pipe individual heating system
The two-pipe scheme of the individual heating network of the apartment includes the following elements:
- heating boiler;
- thermostatic valves for radiators;
- automatic air valve;
- balancing device;
- pipes and fittings;
- radiators;
- valves and taps;
- expansion tank;
- filter;
- temperature gauge;
- circulation pump (if necessary);
- safety valves.
Installation of a two-pipe heating system with top and bottom wiring
The two-pipe system has varieties according to the installation scheme. The most commonly used top and bottom wiring types.
Top wiring
Laying the upper wiring involves installation work to fix the heating system under the ceiling of the room. Batteries installed in places where cold air accumulates (window openings, balcony doors) are supplied with branches coming from the main pipeline. Liquid enters the lower part of the pipeline, which is a bypass, and cools down during circulation. Such a system is suitable for large premises; in one-room or two-room apartments, installation of heating with an upper wiring is not recommended, since this is unprofitable for the owner from an economic and design point of view.
Installation of a heating circuit with an upper horizontal wiring is carried out according to the following scheme:
- An angle fitting, necessary for connecting a pipe directed upwards, is mounted to the boiler outlet.
- With the help of tees and corners, a horizontal installation of the upper line is carried out: the tees are installed above the battery, the corners are on the sides.
- The final stage of the installation of the upper horizontal is the installation of tees with pipes on the battery, supplemented by a shut-off valve.
- On the lower branch, the outlet ends are connected to a common return line, on the section of which an injection pumping station (circulation pump) is installed.
Bottom wiring
In a network with a lower wiring, outlet channels and supply heat pipes are installed. The superiority of the lower mounting scheme is expressed as follows:
- Heating pipes are located in the lower, inconspicuous part of the room, which gives more opportunities for the implementation of various design projects.
- Minimum consumption of pipes: all installation work is carried out practically at the same level. The wiring point and radiator pipes are located at a short distance from each other.
- Due to the simplicity of the scheme, the installation of such a system will be possible even for a non-professional.
Important! The lower wiring is installed only if the circulation of the coolant is forced, otherwise the water will not move through the heating pipes. This scheme is applicable only in city apartments or one-story buildings.
One of the disadvantages of the circuit is the complexity of adjustment and balancing, but the ease of installation and reliability in operation covers these shortcomings.
- Installation work begins with a drain from the boiler nozzles using an angle fitting in a downward direction.
- Wiring is carried out at floor level along the wall using two pipes of the same diameter. One of them connects the boiler pipe to the battery inlet, the other is connected to the receiving pipeline.
- Connections of radiators with pipes are made using tees.
- The expansion tank is located at the highest point of the supply pipe.
- The end of the outlet pipe is connected to the circulation pump, the pump itself is located at the entrance to the heating tank.